 MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences/Duke University
MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences/Duke University
A drug has increased the lifespans of laboratory animals by nearly 25%, in a discovery scientists hope can slow human ageing too.
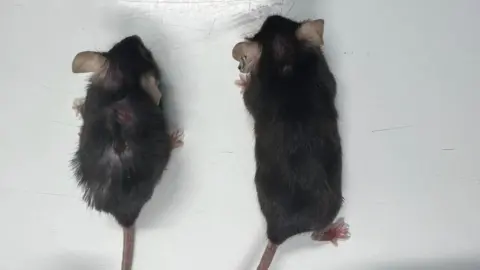
The treated mice were known as "supermodel grannies" in the lab because of their youthful appearance.
They were healthier, stronger and developed fewer cancers than their unmedicated peers.
The drug is already being tested in people, but whether it would have the same anti-ageing effect is unknown.
The quest for a longer life is woven through human history.
However, scientists have long known the ageing process is malleable - laboratory animals live longer if you significantly cut the amount of food they eat.
Now the field of ageing-research is booming as researchers try to uncover - and manipulate - the molecular processes of ageing.
The team at the MRC Laboratory of Medical Science, Imperial College London and Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore were investigating a protein called interleukin-11.
Levels of it increase in the human body as we get older, it contributes to higher levels of inflammation, and the researchers say it flips several biological switches that control the pace of ageing.
Longer, healthier lives
The researchers performed two experiments.
- The first genetically engineered mice so they were unable to produce interleukin-11
- The second waited until mice were 75 weeks old (roughly equivalent to a 55-year-old person) and then regularly gave them a drug to purge interleukin-11 from their bodies
The results, published in the journal Nature, showed lifespans were increased by 20-25% depending on the experiment and sex of the mice.
Old laboratory mice often die from cancer, however, the mice lacking interleukin-11 had far lower levels of the disease.
And they showed improved muscle function, were leaner, had healthier fur and scored better on many measures of frailty.
I asked one of the researchers, Prof Stuart Cook, whether the data was too good to be believed.
He told me: "I try not to get too excited, for the reasons you say, is it too good to be true?
"There's lots of snake oil out there, so I try to stick to the data and they are the strongest out there."
He said he "definitely" thought it was worth trialling in human ageing, arguing that the impact "would be transformative" if it worked and was prepared to take it himself.
But what about people?
The big unanswered questions are could the same effect be achieved in people, and whether any side effects would be tolerable.
Interleukin-11 does have a role in the human body during early development.
People are, very rarely, born unable to make it. This alters how the bones in their skull fuse together, affects their joints, which can need surgery to correct, and how their teeth emerge. It also has a role in scarring.
The researchers think that later in life, interleukin-11 is playing the bad role of driving ageing.
The drug, a manufactured antibody that attacks interleukin-11, is being trialled in patients with lung fibrosis. This is where the lungs become scarred, making it harder to breathe.
Prof Cook said the trials had not been completed, however, the data suggested the drug was safe to take.
This is just the latest approach to "treating" ageing with drugs. The type-2 diabetes drug metformin and rapamycin, which is taken to prevent an organ transplant being rejected, are both actively being researched for their anti-ageing qualities.
Prof Cook thinks a drug is likely to be easier for people than calorie restriction.
"Would you want to live from the age of 40, half-starved, have a completely unpleasant life, if you're going to live another five years at the end? I wouldn't," he said.

 Duke-NUS Medical School
Duke-NUS Medical School
Prof Anissa Widjaja, from Duke-NUS Medical School, said: “Although our work was done in mice, we hope that these findings will be highly relevant to human health, given that we have seen similar effects in studies of human cells and tissues.
“This research is an important step toward better understanding ageing and we have demonstrated, in mice, a therapy that could potentially extend healthy ageing.”
Ilaria Bellantuono, professor of musculoskeletal ageing at the University of Sheffield, said: “Overall, the data seems solid, this is another potential therapy targeting a mechanism of ageing, which may benefit frailty."
However, he said there were still problems, including the lack of evidence in patients and the cost of making such drugs and "it is unthinkable to treat every 50-year-old for the rest of their life".