
ChatGPT was released in November 2022. Since then, we’ve witnessed rapid advancements in the field of AI and technology.
But did you know that the journey of AI chatbots began way back in 1966 with ELIZA? ELIZA was not as sophisticated as today’s models like GPT, but it marked the beginning of the exciting path that led us to where we are now.
Language is the essence of human interaction, and in the digital age, teaching machines to understand and generate language has become a cornerstone of artificial intelligence.
The models we interact with today—such as GPT, Llama3, Gemini, and Claude—are known as Large Language Models (LLMs). This is because they are trained on vast datasets of text, enabling them to perform a wide range of language-related tasks.
But what exactly are LLMs, and why is there so much hype surrounding them?
In this article, you'll learn what LLMs are and what is the hype all about.
Large Language Models are AI models trained on vast amounts of text data to understand, generate, and manipulate human language. They are based on deep learning architectures like transformers, which allow them to process and predict text in a way that mimics human understanding.
In simpler terms, an LLM is a computer program that has been trained on many examples to differentiate between an apple and a Boeing 787 – and to be able to describe each of them.
Before they're ready for use and can answer your questions, LLMs are trained on massive datasets. Realistically, a program cannot conclude anything from a single sentence. But after analyzing, say, trillions of sentences, it's able to build a logic to complete sentences or even generate its own.
How to Train an LLM
Here’s how the training process works:
Data Collection: The first step involves gathering millions (or even billions) of text documents from diverse sources, including books, websites, research papers, and social media. This extensive dataset serves as the foundation for the model’s learning process.
Learning Patterns: The model analyzes the collected data to identify and learn patterns in the text. These patterns include grammar rules, word associations, contextual relationships, and even some level of common sense. By processing this data, the model begins to understand how language works.
Fine-Tuning: After the initial training, the model is fine-tuned for specific tasks. This involves adjusting the model’s parameters to optimize its performance for tasks such as translation, summarization, sentiment analysis, or question-answering.
Evaluation and Testing: Once trained, the model is rigorously tested against a series of benchmarks to evaluate its accuracy, efficiency, and reliability. This step ensures that the model performs well in real-world applications.
After the training process is completed, the models are heavily tested on a series of benchmarks for accuracy, efficiency, security, and so on.
Applications of LLMs
LLMs have a wide range of applications, from content generation to prediction and a lot more.
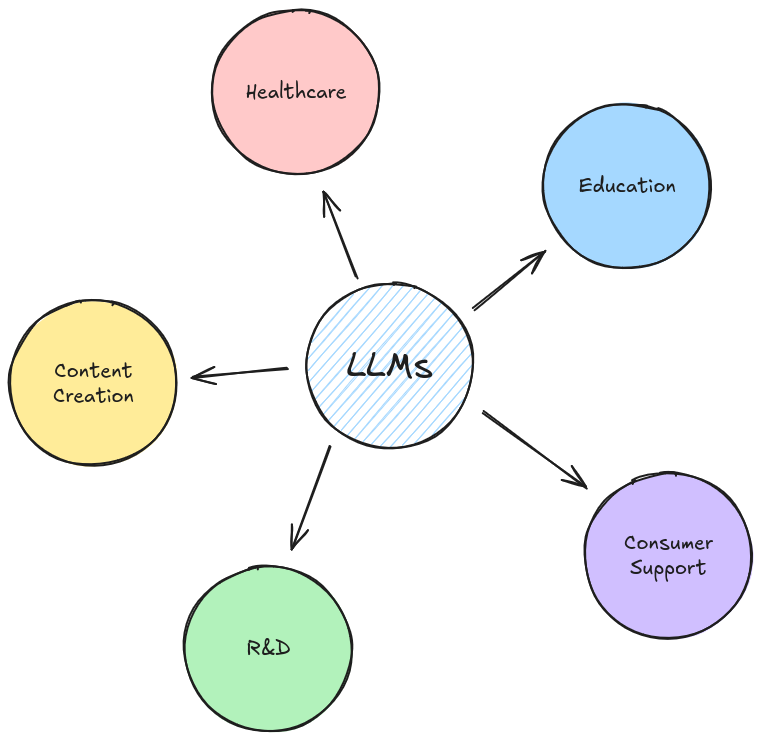
Content Creation:
Writing Assistance: Tools like Grammarly utilize LLMs to provide real-time suggestions for improving grammar, style, and clarity in writing. Whether you’re drafting an email or writing a novel, LLMs can help you polish your text.
Automated Storytelling: AI models can now generate creative content, from short stories to full-length novels. These models can emulate the style of famous authors or even create entirely new literary styles.
Customer Service:
Chatbots: Many companies deploy AI-powered chatbots that can understand and respond to customer inquiries in real time. These chatbots can handle a wide range of tasks, from answering frequently asked questions to processing orders.
Personal Assistants: Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa use LLMs to interpret and respond to voice commands, providing users with information, reminders, and entertainment on demand.
Healthcare:
Medical Record Summarization: LLMs can assist healthcare professionals by summarizing patient records, making it easier to review critical information and make informed decisions.
Diagnostic Assistance: AI models can analyze patient data and medical literature to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases and recommending treatments.
Research and Education:
Literature Review: LLMs can sift through vast amounts of research papers to provide concise summaries, identify trends, and suggest new research directions.
Educational Tools: AI-powered tutors can offer personalized learning experiences by adapting to a student’s progress and needs. These tools can provide instant feedback and tailored study plans.
Entertainment:
Game Development: LLMs are used to create more dynamic and responsive characters in video games. These AI-driven characters can engage with players more realistically and interactively.
Music and Art Generation: AI models are now capable of composing music, generating artwork, and even writing scripts for movies, pushing the boundaries of creative expression.
Challenges with LLMs
While LLMs are powerful, they are not without their challenges. ChatGPT has over 150 Million monthly users, this gives us an idea about how big the impact of AI is. But new technologies pose some challenges too.
Bias and Fairness:
- LLMs learn from the data they are trained on, which can include biases present in society. This can lead to biased or unfair outcomes in their predictions or responses. Addressing this requires careful dataset curation and algorithm adjustments to minimize bias.
Data Privacy:
- LLMs may inadvertently learn and retain sensitive information from the data they are trained on, raising privacy concerns. There’s ongoing research on how to make LLMs more privacy-preserving.
Resource Intensive:
- Training LLMs require immense computational power and large datasets, which can be costly and environmentally taxing. Efforts are being made to create more efficient models that require less energy and data.
Interpretability:
- LLMs are often seen as "black boxes," meaning it’s challenging to understand exactly how they arrive at certain conclusions. Developing methods to make AI more interpretable and explainable is an ongoing research area.
Coding with LLMs: A Replicate Example
For those of you who like to get your hands dirty with code, here’s a quick example of how to use an LLM with the Replicate library.
Replicate is a Python package that simplifies the process of running machine learning models in the cloud. It provides a user-friendly interface to access and utilize a vast collection of pre-trained models from the Replicate platform.
With Replicate, you can easily:
Run models directly from your Python code or Jupyter notebooks.
Access various model types, including image generation, text generation, and more.
Leverage powerful cloud infrastructure for efficient model execution.
Integrate AI capabilities into your applications without the complexities of model training and deployment.
Here’s a simple code snippet to generate text using Meta's llama3-70b-instruct model. Llama 3 is one of the latest open-source large language models developed by Meta. It's designed to be highly capable, versatile, and accessible, allowing users to experiment, innovate, and scale their AI applications.
import os
import replicate # pip install replicate
# Get your token from -> https://replicate.com/account/api-tokens
os.environ["REPLICATE_API_TOKEN"] = "TOKEN"
api = replicate.Client(api_token=os.environ["REPLICATE_API_TOKEN"])
# Running llama3 model using replicate
output = api.run(
"meta/meta-llama-3-70b-instruct",
input={"prompt": 'Hey how are you?'}
)
# Printing llama3's response
for item in output:
print(item, end="")
Explanation:
We first save the replicate token using the os package as an environment variable.
Then we use the Llama3 70b-instruct model to give a response based on our prompt. You can customize the output by changing the prompt.
And what is a prompt? A prompt is essentially a text-based instruction or query given to an AI model. It's like providing a starting point or direction for the AI to generate text, translate languages, write different kinds of creative content, and answer your questions in an informative way.
For example:
"Write a poem about a robot exploring the ocean."
"Translate 'Hello, how are you?' into Spanish."
"Explain quantum computing in simple terms."
These are all prompts that guide the AI to produce a specific output.
Using Meta's llama-3-70b-instruct, you can build various tools around applications that are mentioned in this article. Tweak the prompts based on your use case and you will be ready to go! ⚡️
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the world of Large Language Models, providing a high-level understanding of how they work and their training process. We delved into the core concepts of LLMs, including data collection, pattern learning, and fine-tuning, and discussed the extensive applications of LLMs across various industries.
While LLMs offer immense potential, they also come with challenges such as bias, privacy concerns, resource demands, and interpretability. Addressing these challenges is crucial as AI continues to evolve and integrate more deeply into our lives.
We also provided a glimpse into how you can start working with LLMs using the Replicate library, showing that even complex models like Llama3 70b-instruct can be accessible to developers with the right tools.