Editor’s note: This article was last updated on 27 August 2004 to bolster the step-by-step guide with more detailed instructions, more robust examples, and a downloadable, customizable template.
Opportunities are everywhere. Some opportunities are small and don’t require many resources. Others are massive and need further analysis and evaluation.
One of your key responsibilities as a product manager is to evaluate the potential success of those opportunities before investing significant money, time, and resources. A feasibility study, also known as a feasibility assessment or feasibility analysis, is a critical tool that can help product managers determine whether a product idea or opportunity is viable, feasible, and profitable.
So, what is a feasibility analysis? Why should product managers use it? And how do you conduct one?
Click here to download our customizable feasibility study template.
What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study is a systematic analysis and evaluation of a product opportunity’s potential to succeed. It aims to determine whether a proposed opportunity is financially and technically viable, operationally feasible, and commercially profitable.
A feasibility study typically includes an assessment of a wide range of factors, including the technical requirements of the product, resources needed to develop and launch the product, the potential market gap and demand, the competitive landscape, and economic and financial viability. These factors can be broken down into different types of feasibility studies:
- Technical feasibility — Evaluates the technical resources and expertise needed to develop the product and identifies any technical challenges that could arise
- Financial feasibility — Analyzes the costs involved, potential revenue, and overall financial viability of the opportunity
- Market feasibility — Assesses the demand for the product, market trends, target audience, and competitive landscape
- Operational feasibility — Looks at the organizational structure, logistics, and day-to-day operations required to launch and sustain the product
- Legal feasibility — Examines any legal considerations, including regulations, patents, and compliance requirements that could affect the opportunity
Based on the analysis’s findings, the product manager and their product team can decide whether to proceed with the product opportunity, modify its scope, or pursue another opportunity and solve a different problem.
Conducting a feasibility study helps PMs ensure that resources are invested in opportunities that have a high likelihood of success and align with the overall objectives and goals of the product strategy.
What are feasibility analyses used for?
Feasibility studies are particularly useful when introducing entirely new products or verticals. Product managers can use the results of a feasibility study to:
- Assess the technical feasibility of a product opportunity — Evaluate whether the proposed product idea or opportunity can be developed with the available technology, tools, resources, and expertise
- Determine a project’s financial viability — By analyzing the costs of development, manufacturing, and distribution, a feasibility study helps you determine whether your product is financially viable and can generate a positive return on investment (ROI)
- Evaluate customer demand and the competitive landscape — Assessing the potential market size, target audience, and competitive landscape for the product opportunity can inform decisions about the overall product positioning, marketing strategies, and pricing
- Identify potential risks and challenges — Identify potential obstacles or challenges that could impact the success of the identified opportunity, such as regulatory hurdles, operational and legal issues, and technical limitations
- Refine the product concept — The insights gained from a feasibility study can help you refine the product’s concept, make necessary modifications to the scope, and ultimately create a better product that is more likely to succeed in the market and meet users’ expectations
How to conduct a feasibility study
The activities involved in conducting a feasibility study differ from one organization to another. Also, the threshold, expectations, and deliverables change from role to role. However, a general set of guidelines can help you get started.
Here are some basic steps to conduct and report a feasibility study for major product opportunities or features:
1. Clearly define the opportunity
Imagine your user base is facing a significant problem that your product doesn’t solve. This is an opportunity. Define the opportunity clearly, support it with data, talk to your stakeholders to understand the opportunity space, and use it to define the objective.
2. Define the objective and scope
Each opportunity should be coupled with a business objective and should align with your product strategy.
Determine and clearly communicate the business goals and objectives of the opportunity. Align those objectives with company leaders to make sure everyone is on the same page. Lastly, define the scope of what you plan to build.
3. Conduct market and user research
Now that you have everyone on the same page and the objective and scope of the opportunity clearly defined, gather data and insights on the target market.
Include elements like the total addressable market (TAM), growth potential, competitors’ insights, and deep insight into users’ problems and preferences collected through techniques like interviews, surveys, observation studies, contextual inquiries, and focus groups.
4. Analyze technical feasibility
Suppose your market and user research have validated the problem you are trying to solve. The next step should be to, alongside your engineers, assess the technical resources and expertise needed to launch the product to the market.
Dig deeper into the proposed solution and try to comprehend the technical limitations and estimated time required for the product to be in your users’ hands. A detailed assessment might include:
- Technical requirements — What technology stack is needed? Does your team have the necessary expertise? Are there any integration challenges?
- Development timeline — How long will it take to develop the solution? What are the critical milestones?
- Resource allocation — What resources (hardware, software, personnel) are required? Can existing resources be repurposed?
5. Assess financial viability
If your company has a product pricing team, work closely with them to determine the willingness to pay (WTP) and devise a monetization strategy for the new feature.
Conduct a comprehensive financial analysis, including the total cost of development, revenue streams, and the expected return on investment (ROI) based on the agreed-upon monetization strategy. Key elements to include:
- Cost analysis — Breakdown of development, production, and operational costs
- Revenue projections — Estimated revenue from different pricing models
- ROI calculation — Expected return on investment and payback period
6. Evaluate potential risks
Now that you have almost a complete picture, identify the risks associated with building and launching the opportunity. Risks may include things like regulatory hurdles, technical limitations, and any operational risks.
A thorough risk assessment should cover:
- Technical risks — Potential issues with technology, integration, or scalability.
- Market risks — Changes in market conditions, customer preferences, or competitive landscape.
- Operational risks — Challenges in logistics, staffing, or supply chain management.
- Regulatory risks — Legal or compliance issues that could affect the product’s launch. For more on regulatory risks, check out this Investopedia article.
7. Decide, prepare, and share
Based on the steps above, you should end up with a comprehensive report that helps you decide whether to pursue the opportunity, modify its scope, or explore alternative options. Here’s what you should do next:
- Prepare your report — Compile all your findings, including the feasibility analysis, market research, technical assessment, financial viability, and risk analysis into a detailed report. This document should provide a clear recommendation on whether to move forward with the project
- Create an executive summary — Summarize the key findings and recommendations in a concise executive summary, tailored for stakeholders such as the C-suite. The executive summary should capture the essence of your report, focusing on the most critical points
- Present to stakeholders — Share your report with stakeholders, ensuring you’re prepared to discuss the analysis and defend your recommendations. Make sure to involve key stakeholders early in the process to build buy-in and address any concerns they may have
- Prepare for next steps — Depending on the decision, be ready to either proceed with the project, implement modifications, or pivot to another opportunity. Outline the action plan, resource requirements, and timeline for the next phase
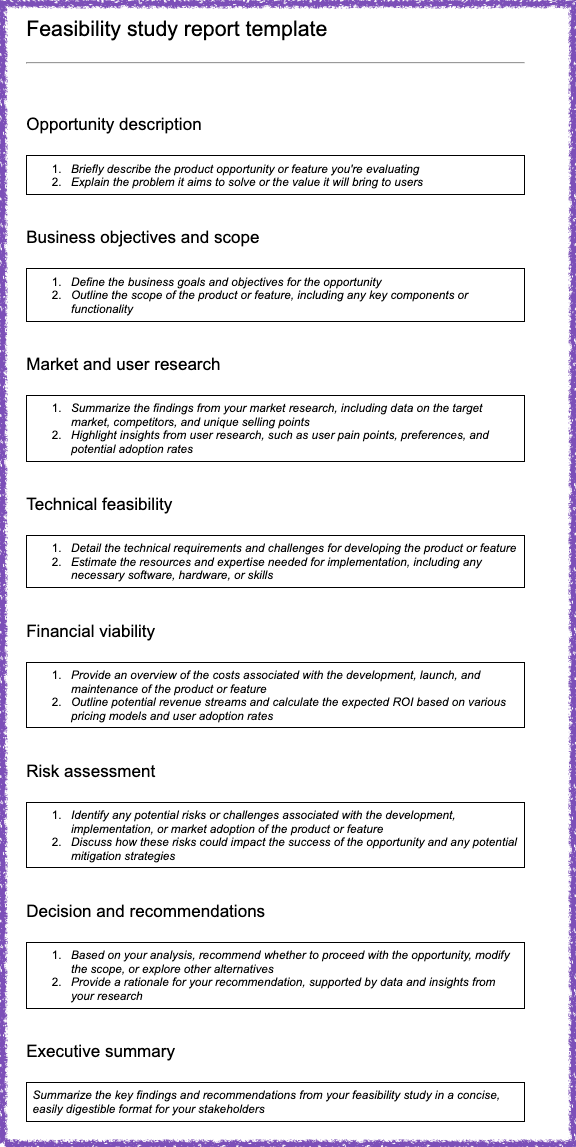
Feasibility study template
The following feasibility study report template is designed to help you evaluate the feasibility of a product opportunity and provide a comprehensive report to inform decision-making and guide the development process.
Note: You can customize this template to fit your specific needs. Click here to download and customize this feasibility study report template.
Feasibility study example
Imagine you’re a product manager at a company that specializes in project management tools. Your team has identified a potential opportunity to expand the product offering by developing a new AI-powered feature that can automatically prioritize tasks for users based on their deadlines, workload, and importance.
A feasibility study can help you assess the viability of this opportunity. Here’s how you might approach it according to the template above:
1. Clearly define the opportunity
- Opportunity description — The opportunity lies in creating an AI-powered feature that automatically prioritizes tasks based on user-defined parameters such as deadlines, workload, and task importance. This feature is expected to enhance user productivity by helping teams focus on high-priority tasks and ensuring timely project completion
- Problem statement — Many users of project management tools struggle with managing and prioritizing tasks effectively, leading to missed deadlines and project delays. Current solutions often require manual input or lack sophisticated algorithms to adjust priorities dynamically. The proposed AI-powered feature aims to solve this problem by automating the prioritization process, thereby reducing manual effort and improving overall project efficiency
2. Define the objective and scope
- Business objective — The primary objective is to increase user engagement and satisfaction by offering a feature that addresses a common pain point. The feature is also intended to increase customer retention by providing added value and driving user adoption
- Scope — The scope includes the development of an AI algorithm capable of analyzing task parameters (e.g., deadlines, workload) and dynamically prioritizing tasks. The feature will be integrated into the existing project management tool interface, with minimal disruption to current users. Additionally, the scope covers user training and support for the new feature
3. Conduct market and user research
Market analysis:
- Total addressable market (TAM) — The TAM for this feature includes all users who actively manage projects and could benefit from enhanced task prioritization
- Competitor analysis — Competitor products such as Asana and Trello offer basic task prioritization features, but none use advanced AI algorithms. This presents a unique opportunity to differentiate this product by offering a more sophisticated solution
- User pain points — Surveys and interviews with current users reveal that 65 percent struggle with manual task prioritization, leading to inefficiencies and missed deadlines. Users expressed a strong interest in an automated solution that could save time and improve project outcomes
4. Analyze technical feasibility
Technical requirements:
- AI algorithm development — The core of the feature is an AI algorithm that can analyze multiple factors to prioritize tasks. This requires expertise in machine learning, data processing, and AI integration
- Integration with existing infrastructure — The feature must seamlessly integrate with the existing architecture without causing significant disruptions. This includes data compatibility, API development, and UI/UX considerations
- Data handling and privacy — The feature will process sensitive project data, so robust data privacy and security measures must be implemented to comply with regulations like GDPR
Development timeline:
- Phase 1 (3 months) — Research and development of the AI algorithm, including training with sample datasets
- Phase 2 (2 months) — Integration with the platform, including UI/UX design adjustments
- Phase 3 (1 month) — Testing, quality assurance, and bug fixing
- Phase 4 (1 month) — User training materials and documentation preparation
Resource allocation:
- Development team — Two AI specialists, three backend developers, two frontend developers, one project manager
- Hardware/software — Additional cloud computing resources for AI processing, development tools for machine learning, testing environments
5. Assess financial viability
Cost analysis:
- Development costs — Estimated at $300,000, including salaries, cloud computing resources, and software licenses
- Marketing and launch costs — $50,000 for promotional activities, user onboarding, and initial support
- Operational costs — $20,000/year for maintenance, AI model updates, and ongoing support
Revenue projections:
- Pricing model — The AI-powered feature will be offered as part of a premium subscription tier, with an additional monthly fee of $10/user
- User adoption — Based on user surveys, an estimated 25 percent of the current user base (10,000 users) is expected to upgrade to the premium tier within the first year
- Projected revenue — First-year revenue is projected at $1.2 million, with an expected growth rate of 10 percent annually
ROI calculation:
- Break-even point — The project is expected to break even within 6 months of launch
- Five-year ROI — The feature is projected to generate a 200% ROI over five years, driven by increased subscription fees and user retention
6. Evaluate potential risks
Technical risks:
- AI algorithm complexity — Developing an accurate and reliable AI algorithm is challenging and may require multiple iterations
- Integration issues — There is a risk that integrating the new feature could disrupt the existing platform, leading to user dissatisfaction
Market risks:
- User adoption — There’s a risk that users may not perceive sufficient value in the AI feature to justify the additional cost, leading to lower-than-expected adoption rates
Operational risks:
- Support and maintenance — Maintaining the AI feature requires continuous updates and monitoring, which could strain the development and support teams
Regulatory risks:
- Data privacy compliance — Handling sensitive project data requires strict adherence to data privacy regulations. Noncompliance could lead to legal challenges and damage to the company’s reputation
7. Decide, prepare, and share
- Decision — Based on the comprehensive analysis, the recommendation is to proceed with the development and launch of the AI-powered task prioritization feature. The potential for increased user engagement, differentiation from competitors, and positive ROI justifies the investment
- Prepare the report — A detailed report will be compiled, including all findings from the feasibility study, cost-benefit analysis, and risk assessments. This report will be presented to key stakeholders for approval
- Create an executive summary — A concise executive summary will be prepared for the C-suite, highlighting the key benefits, expected ROI, and strategic alignment with the company’s goals
- Next steps — Upon approval, the project will move into the development phase, following the timeline and resource allocation outlined in the study. Continuous monitoring and iterative improvements will be made based on user feedback and performance metrics
8. Executive summary
This feasibility study evaluates the potential for developing and launching an AI-powered task prioritization feature within our project management tool. The feature is intended to automatically prioritize tasks based on deadlines, workload, and task importance, thus improving user productivity and project efficiency. The study concludes that the feature is both technically and financially viable, with a projected ROI of 200 percent over five years. The recommendation is to proceed with development, as the feature offers a significant opportunity for product differentiation and user satisfaction.
Mock feasibility study report
Now let’s see what a feasibility study report based on the above example scenario would look like (download an example here):
Introduction
The purpose of this feasibility study is to assess the viability of introducing an AI-powered task prioritization feature into our existing project management software. This feature aims to address the common user challenge of manually prioritizing tasks, which often leads to inefficiencies and missed deadlines. By automating this process, we expect to enhance user productivity, increase customer retention, and differentiate our product in a competitive market.
Market and user research
The total addressable market (TAM) for this AI-powered task prioritization feature includes all current and potential users of project management tools who manage tasks and projects regularly. Based on market analysis, the current user base primarily consists of mid-sized enterprises and large organizations, where task management is a critical component of daily operations.
- Competitor analysis — Key competitors in the project management space, such as Asana and Trello, offer basic task prioritization features. However, these solutions lack advanced AI capabilities that dynamically adjust task priorities based on real-time data. This gap in the market presents an opportunity for us to differentiate our product by offering a more sophisticated, AI-driven solution
- User pain points — Surveys and interviews conducted with our current user base reveal that 65 percent of users experience challenges with manual task prioritization. Common issues include difficulty in maintaining focus on high-priority tasks, inefficient use of time, and the tendency to miss deadlines due to poor task management. Users expressed a strong interest in an automated solution that could alleviate these challenges, indicating a high demand for the proposed feature
Technical feasibility
- AI algorithm development — The core component of the feature is an AI algorithm capable of analyzing multiple task parameters, such as deadlines, workload, and task importance. The development of this algorithm requires expertise in machine learning, particularly in natural language processing (NLP) and predictive analytics. Additionally, data processing capabilities will need to be enhanced to handle the increased load from real-time task prioritization
- Integration with existing infrastructure — The AI-powered feature must be integrated into our existing project management tool with minimal disruption. This includes ensuring compatibility with current data formats, APIs, and the user interface. The integration will also require modifications to the UI/UX to accommodate the new functionality while maintaining ease of use for existing features
- Data handling and privacy — The feature will process sensitive project data, making robust data privacy and security measures critical. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR is mandatory, and the data flow must be encrypted end-to-end to prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, user consent will be required for data processing related to the AI feature
Development timeline:
- Phase 1 (3 months) — Research and development of the AI algorithm, including dataset acquisition, model training, and initial testing
- Phase 2 (2 months) — Integration with the existing platform, focusing on backend development and UI/UX adjustments
- Phase 3 (1 month) — Extensive testing, quality assurance, and bug fixing to ensure stability and performance
- Phase 4 (1 month) — Development of user training materials, documentation, and preparation for the product launch
Financial analysis
Cost analysis:
- Development costs — Estimated at $300,000, covering salaries, cloud computing resources, machine learning tools, and necessary software licenses
- Marketing and launch costs — $50,000 allocated for promotional campaigns, user onboarding programs, and initial customer support post-launch
- Operational costs — $20,000 annually for ongoing maintenance, AI model updates, and customer support services
Revenue projections:
- Pricing model — The AI-powered task prioritization feature will be included in a premium subscription tier, with an additional monthly fee of $10 per user
- User adoption — Market research suggests that approximately 25% of the current user base (estimated at 10,000 users) is likely to upgrade to the premium tier within the first year
- Projected revenue — First-year revenue is estimated at $1.2 million, with an anticipated annual growth rate of 10% as more users adopt the feature
ROI calculation:
- Break-even point — The project is expected to reach its break-even point within 6 months of the feature’s launch
- Five-year ROI — Over a five-year period, the feature is projected to generate a return on investment (ROI) of 200 percent, driven by steady subscription revenue and enhanced user retention
Risk assessment
Technical risks:
- AI algorithm complexity — Developing a sophisticated AI algorithm poses significant technical challenges, including the risk of inaccuracies in task prioritization. Multiple iterations and extensive testing will be required to refine the algorithm
- Integration issues — Integrating the new feature into the existing platform could potentially cause compatibility issues, resulting in performance degradation or user dissatisfaction
Market risks:
- User adoption — There is a possibility that users may not perceive enough value in the AI-powered feature to justify the additional cost, leading to lower-than-expected adoption rates and revenue
Operational risks:
- Support and maintenance — The ongoing support and maintenance required for the AI feature, including regular updates and monitoring, could place a significant burden on the development and customer support teams, potentially leading to resource constraints
Regulatory risks:
- Data privacy compliance — Handling sensitive user data for AI processing necessitates strict adherence to data privacy regulations such as GDPR. Failure to comply could result in legal repercussions and damage to the company’s reputation
Conclusion and recommendations
The feasibility study demonstrates that the proposed AI-powered task prioritization feature is both technically and financially viable. The feature addresses a significant user pain point and has the potential to differentiate the product in a competitive market. With an estimated ROI of 200 percent over five years and strong user interest, it is recommended that the project move forward into the development phase.
Next steps include finalizing the development plan, securing approval from key stakeholders, and initiating the development process according to the outlined timeline and resource allocation. Continuous monitoring and iterative improvements will be essential to ensure the feature meets user expectations and achieves the projected financial outcomes.
Overcoming stakeholder management challenges
The ultimate challenge that faces most product managers when conducting a feasibility study is managing stakeholders.
Stakeholders may interfere with your analysis, jumping to conclusions that your proposed product or feature won’t work and deeming it a waste of resources. They may even try to prioritize your backlog for you.
Here are some tips to help you deal with even the most difficult stakeholders during a feasibility study:
- Use hard data to make your point — Never defend your opinion based on your assumptions. Always show them data and evidence based on your user research and market analysis
- Learn to say no — You are the voice of customers, and you know their issues and how to monetize them. Don’t be afraid to say no and defend your team’s work as a product manager
- Build stakeholder buy-in early on — Engage stakeholders from the beginning of the feasibility study process by involving them in discussions and seeking their input. This helps create a sense of ownership and ensures that their concerns and insights are considered throughout the study
- Provide regular updates and maintain transparency — Keep stakeholders informed about the progress of the feasibility study by providing regular updates and sharing key findings. This transparency can help build trust, foster collaboration, and prevent misunderstandings or misaligned expectations
- Leverage stakeholder expertise — Recognize and utilize the unique expertise and knowledge that stakeholders bring to the table. By involving them in specific aspects of the feasibility study where their skills and experience can add value, you can strengthen the study’s outcomes and foster a more collaborative working relationship
Final thoughts
A feasibility study is a critical tool to use right after you identify a significant opportunity. It helps you evaluate the potential success of the opportunity, analyze and identify potential challenges, gaps, and risks in the opportunity, and provides a data-driven approach in the market insights to make an informed decision.
By conducting a feasibility study, product teams can determine whether a product idea is profitable, viable, feasible, and thus worth investing resources into. It is a crucial step in the product development process and when considering investments in significant initiatives such as launching a completely new product or vertical.
For a more detailed approach and ready-to-use resources, consider using the feasibility study template provided in this post. If you’re dealing with challenging stakeholders, remember the importance of data-driven decisions, maintaining transparency, and leveraging the expertise of your team.